Amber Route - History, Significance, and Travel Guide
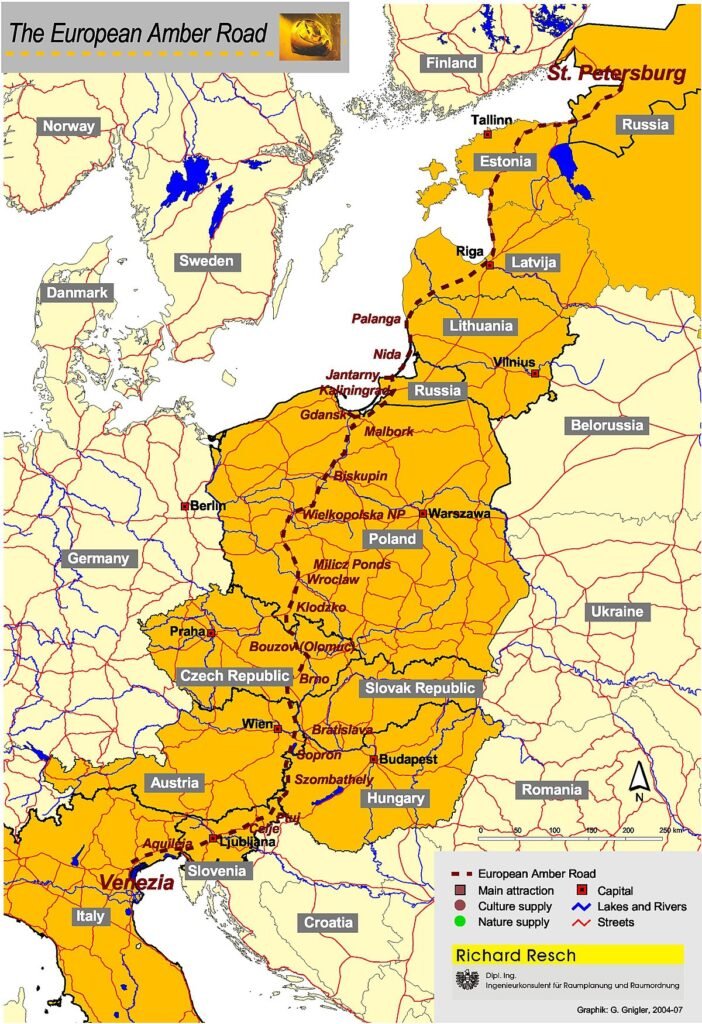
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating history of the Amber Route, an ancient trade network that connected the Baltic Sea with the Mediterranean. We will explore its origins, its peak during the Roman Empire, and its role in facilitating economic and cultural exchanges across Europe.
We will also discuss the significance of the Amber Route, highlighting how it contributed to the development of the regions it traversed by enabling the movement of goods, ideas, and technologies.
Finally, we will provide a travel guide for modern adventurers interested in retracing this historic path. Key destinations, historical sites, and practical travel tips will be covered to help you plan a journey that combines historical exploration with the enjoyment of natural landscapes.
Historical background of the Amber Route
The Amber Route traces its origins back to prehistoric times, when amber, often referred to as "the gold of the north," was highly prized for its beauty and supposed mystical properties. This fossilized tree resin, primarily found along the shores of the Baltic Sea, became a sought-after commodity in ancient civilizations, including those of the Mediterranean. The route itself was not a single path but rather a network of interconnected trails and waterways that facilitated the movement of amber from northern Europe to the south.
During the Roman Empire, the Amber Route reached its peak significance. The Romans, fascinated by amber's allure and utility, established well-defined trade routes to ensure a steady supply of this precious material. Roman merchants and traders traveled through what are now modern-day Poland, Germany, Austria, and Italy, exchanging amber for goods such as wine, spices, and luxury items. This exchange not only boosted economic prosperity but also fostered cultural and technological exchanges between the diverse regions connected by the route.
Archaeological evidence, including ancient roads, trading posts, and artifacts, attests to the extensive use and importance of the Amber Route. The route's legacy is also preserved in historical texts and records, which highlight the strategic and economic value of amber in ancient trade networks. Today, the Amber Route stands as a testament to the ingenuity and interconnectedness of early civilizations, offering a fascinating glimpse into the past for historians and travelers alike.
The significance of amber in ancient times
Amber held immense value in ancient times, not only for its aesthetic appeal but also for its perceived mystical and medicinal properties. This fossilized tree resin, often found in shades of golden yellow to deep orange, was highly prized by various cultures for its beauty and rarity. It was commonly used in jewelry, amulets, and decorative objects, symbolizing wealth and status. The allure of amber extended beyond its visual charm; it was believed to possess protective and healing powers, making it a sought-after material for talismans and medicinal concoctions.
In addition to its ornamental and mystical uses, amber played a crucial role in the economic and cultural exchanges facilitated by the Amber Route. As a highly coveted commodity, it became a cornerstone of trade between the Baltic region and the Mediterranean. The demand for amber in the Roman Empire, where it was used in various luxury items and religious artifacts, spurred the development of extensive trade networks. These networks not only transported amber but also facilitated the exchange of other goods, ideas, and technologies, significantly impacting the societies along the route. The trade of amber thus contributed to the interconnectedness of ancient European civilizations, fostering economic prosperity and cultural enrichment.
Key regions and cities along the Amber Route
The Amber Route traverses several key regions and cities, each offering a unique glimpse into the historical and cultural tapestry woven by this ancient trade network. In Poland, the city of Gdańsk stands out as a significant starting point. Known for its rich maritime history and vibrant amber trade, Gdańsk is home to the Amber Museum, where visitors can explore the history and craftsmanship of amber. Moving south, the city of Wrocław, with its picturesque market square and Gothic architecture, serves as another important stop, reflecting the medieval prosperity brought by the amber trade.
In Germany, the city of Leipzig emerges as a crucial hub along the route. Renowned for its trade fairs and vibrant cultural scene, Leipzig's historical significance is underscored by its role in facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. Further south, the Austrian city of Vienna offers a blend of imperial grandeur and artistic heritage. Vienna's museums and historic sites provide insights into the city's role as a crossroads of trade and culture during the height of the Amber Route's prominence.
The journey culminates in Italy, where the city of Aquileia stands as a testament to the route's southern terminus. Once a major Roman port, Aquileia's archaeological sites and museums offer a window into the ancient world, showcasing the city's importance in the amber trade. Each of these regions and cities not only highlights the historical significance of the Amber Route but also invites travelers to immerse themselves in the rich cultural legacies that continue to shape these destinations today.
Poland: Gdańsk and its amber heritage
Gdańsk, a historic port city on the Baltic coast of Poland, is often considered the heart of the amber trade. Known as the "World Capital of Amber," Gdańsk has a rich history intertwined with this precious resin, which has been harvested from the Baltic Sea for millennia. The city's strategic location made it a crucial hub on the Amber Route, facilitating the exchange of amber with traders from across Europe and beyond.
Visitors to Gdańsk can immerse themselves in its amber heritage through a variety of attractions and experiences. The Amber Museum, housed in the medieval Foregate building, offers a comprehensive look at the history and significance of amber, showcasing exquisite pieces ranging from ancient artifacts to contemporary jewelry. The museum also provides insights into the geological formation of amber and its various uses throughout history.
Strolling through the streets of Gdańsk, travelers will find numerous amber shops and galleries, where skilled artisans continue the tradition of crafting intricate amber jewelry and decorative items. The annual St. Dominic's Fair, one of the largest and oldest trade fairs in Europe, also features a significant amber market, drawing collectors and enthusiasts from around the world. Whether exploring historical sites or shopping for unique souvenirs, Gdańsk offers a captivating glimpse into the enduring legacy of the Amber Route.
Germany: Berlin and the ancient trade connections
Berlin, the vibrant capital of Germany, may not have been a central hub of the Amber Route itself, but its historical and cultural significance offers a fascinating glimpse into the ancient trade connections that once crisscrossed the region. As a city that has long been a melting pot of cultures and ideas, Berlin provides a modern-day reflection of the diverse interactions that the Amber Route facilitated.
In Berlin, visitors can explore the Pergamon Museum, which houses an extensive collection of artifacts from ancient civilizations, including those that were part of the trade networks connected by the Amber Route. The museum's exhibits offer insights into the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies that shaped the ancient world. Additionally, the city's numerous historical sites and monuments, such as the Brandenburg Gate and the Berlin Wall, provide context for understanding the broader historical and cultural dynamics of the region.
For those interested in tracing the ancient trade connections more directly, Berlin serves as an excellent starting point for journeys to other key locations along the Amber Route in Germany. From here, travelers can venture to cities like Hamburg and Lübeck, which were significant ports in the Hanseatic League and played crucial roles in the medieval trade of amber and other goods. These cities, with their well-preserved medieval architecture and rich histories, offer a tangible link to the past and a deeper appreciation of the Amber Route's enduring legacy.
Austria: Vienna and its historical importance
Vienna, the capital of Austria, holds a pivotal place in the history of the Amber Route. As a major hub of the Habsburg Empire, Vienna was not only a political and cultural center but also a crucial point of convergence for traders journeying between the Baltic and the Mediterranean. The city's strategic location along the Danube River made it an essential stop for merchants transporting amber and other valuable goods, facilitating the exchange of commodities, ideas, and innovations.
Vienna's rich history is reflected in its stunning architecture and numerous historical sites. The Hofburg Palace, once the imperial winter residence, stands as a testament to the city's grandeur and its role in European history. The Kunsthistorisches Museum, with its extensive collection of art and artifacts, offers insights into the cultural exchanges that took place along the Amber Route. Visitors can also explore the ancient Roman ruins at the Michaelerplatz, which provide a glimpse into Vienna's early connections with the Roman Empire and its significance as a trading post.
Today, Vienna continues to celebrate its historical importance through various cultural events and exhibitions. The city's vibrant atmosphere, combined with its historical landmarks, makes it a compelling destination for travelers tracing the Amber Route. Whether strolling through the historic center, a UNESCO World Heritage site, or enjoying a performance at the Vienna State Opera, visitors can immerse themselves in the rich tapestry of history and culture that defines this remarkable city.
Italy: Venice and the Mediterranean link
Venice, often referred to as the "Queen of the Adriatic," played a pivotal role in the Amber Route as the Mediterranean terminus of this ancient trade network. Renowned for its strategic location and maritime prowess, Venice became a bustling hub where northern European amber was exchanged for Mediterranean goods such as spices, silk, and precious metals. The city's intricate network of canals and its position as a gateway to the East made it an ideal center for commerce and cultural exchange.
The influence of the Amber Route on Venice is evident in the city's architecture, art, and historical records. The wealth generated from trade allowed for the construction of grand palaces, churches, and public buildings, many of which still stand today as testaments to the city's prosperous past. Visitors to Venice can explore landmarks such as the Doge's Palace and St. Mark's Basilica, which reflect the opulence and cosmopolitan nature of the city during its peak as a trading power.
For modern travelers tracing the Amber Route, Venice offers a captivating blend of history, culture, and scenic beauty. Walking through its narrow streets and crossing its iconic bridges, one can imagine the bustling markets and vibrant exchanges that once took place. Museums such as the Museo Correr and the Gallerie dell'Accademia provide deeper insights into the city's rich heritage, showcasing artifacts and artworks that highlight Venice's role in the ancient trade network. Venice not only serves as a historical endpoint of the Amber Route but also as a living museum where the legacy of this ancient trade continues to be celebrated.
Cultural and economic impact of the Amber Route
The Amber Route played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural and economic landscapes of the regions it traversed. Economically, it facilitated the exchange of amber, often referred to as "Baltic gold," which was highly prized in ancient civilizations for its beauty and supposed mystical properties. This trade brought wealth and prosperity to the communities along the route, fostering the development of bustling trade hubs and marketplaces. The influx of goods such as spices, textiles, and metals from the Mediterranean, in exchange for amber and other northern commodities, created a vibrant economic network that spanned much of Europe.
Culturally, the Amber Route served as a conduit for the exchange of ideas, art, and technology. As traders and travelers moved along the route, they brought with them not only goods but also stories, knowledge, and cultural practices. This exchange enriched the local cultures, leading to a blending of traditions and innovations. For instance, Roman influence can be seen in the architecture, language, and artifacts found in regions far from the heart of the empire, indicating the far-reaching impact of this trade network. The Amber Route thus acted as a bridge, connecting diverse cultures and fostering a shared heritage that can still be traced in the archaeological and historical records of the regions it linked.
Modern-day travel along the Amber Route
Modern-day travel along the Amber Route offers a captivating blend of historical exploration and scenic adventure. Starting in the Baltic region, travelers can visit Gdańsk, Poland, a city renowned for its rich amber heritage and vibrant old town. The Amber Museum in Gdańsk provides an excellent introduction to the history and significance of amber, showcasing exquisite artifacts and detailing the ancient trade routes. From there, the journey can continue through Poland, with stops in cities like Wrocław and Kraków, where medieval architecture and historical sites abound.
Crossing into Germany, the route leads to cities such as Leipzig and Nuremberg, each offering a unique glimpse into the past with their well-preserved historical centers and museums. In Leipzig, the Museum of Antiquities houses a collection of Roman artifacts, providing context to the ancient trade connections. Nuremberg, with its impressive castle and old town, offers a deeper dive into the medieval period, highlighting the city's role in European trade networks.
As travelers move further south into Austria, Vienna stands out as a cultural hub with its grand palaces, museums, and vibrant arts scene. The Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna features extensive collections that include Roman antiquities, offering insights into the broader historical context of the Amber Route. Finally, the journey can culminate in Italy, with destinations like Aquileia and Venice. Aquileia, once a major Roman city, now an archaeological site, provides a direct link to the ancient world, while Venice, with its canals and historic trade connections, serves as a fitting end to the route, embodying the spirit of commerce and cultural exchange that defined the Amber Route.
Must-visit museums and historical sites
For those tracing the ancient Amber Route, several must-visit museums and historical sites offer a deep dive into the rich history and cultural significance of this ancient trade network. In Poland, the Gdańsk Archaeological Museum is a prime destination. Located in the heart of Gdańsk, a city historically known for its amber trade, the museum houses an extensive collection of amber artifacts, including intricately carved jewelry and tools, providing insight into the craftsmanship and trade practices of ancient times.
Moving into Germany, the city of Berlin boasts the Neues Museum, which features an impressive collection of artifacts from the ancient world, including pieces related to the Amber Route. The museum's exhibits on prehistoric Europe and the Roman Empire offer context to the broader historical and cultural exchanges facilitated by the trade network. Additionally, the German Amber Museum in Ribnitz-Damgarten is dedicated entirely to amber, showcasing its geological formation, historical significance, and artistic uses.
In Austria, the Carnuntum Archaeological Park near Vienna is a must-see. This site was once a major Roman city and military camp, strategically located along the Amber Route. Visitors can explore reconstructed Roman buildings, including a villa, baths, and an amphitheater, gaining a vivid picture of life during the height of the Roman Empire. The park also hosts numerous artifacts uncovered from the area, illustrating the extensive trade and cultural interactions that took place.
Finally, in Italy, the city of Aquileia is a treasure trove of Roman history. Once a bustling hub at the southern end of the Amber Route, Aquileia's archaeological site and museum offer a wealth of Roman relics, including mosaics, sculptures, and everyday items that tell the story of this ancient trade center. The Basilica of Aquileia, with its stunning early Christian mosaics, is another highlight, reflecting the city's historical and religious significance.
Tips for travelers: planning your journey
When planning your journey along the Amber Route, it's essential to start with thorough research and a well-structured itinerary. Begin by identifying the key destinations you wish to visit, such as Gdańsk in Poland, known for its rich amber history, or the ancient Roman sites in Italy. Each location offers unique historical and cultural experiences, so prioritize based on your interests. Consider the time of year for your trip; summer months provide pleasant weather for exploring outdoor sites, while off-peak seasons might offer fewer crowds and a more intimate experience.
Transportation is another crucial aspect to consider. The Amber Route can be traversed by car, bike, or on foot, depending on your preference and fitness level. Renting a car provides flexibility and the ability to cover more ground quickly, while cycling or hiking offers a more immersive experience. Ensure your mode of transport is suitable for the terrain and distances involved. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local transportation options, such as trains and buses, which can be convenient for certain segments of the route.
Accommodation options along the Amber Route range from modern hotels to charming guesthouses and historic inns. Booking in advance, especially during peak tourist seasons, can save you from last-minute hassles. Look for lodgings that offer easy access to the historical sites and natural attractions you plan to visit. Engaging with local guides or joining organized tours can also enrich your experience, providing deeper insights into the history and significance of the Amber Route.
Conclusion
The Amber Route stands as a testament to the enduring power of trade and cultural exchange in shaping human history. From its origins in prehistoric times to its prominence during the Roman Empire, this ancient network facilitated the movement of amber and other valuable goods, fostering economic prosperity and cultural interactions across Europe. The legacy of the Amber Route is evident in the rich historical and archaeological sites that dot its path, offering modern travelers a unique glimpse into the past.
Today, the Amber Route invites adventurers to retrace the steps of ancient traders, exploring the diverse landscapes and historical landmarks that define this storied corridor. Whether journeying by car, bike, or on foot, travelers can immerse themselves in the vibrant history and natural beauty of regions in Poland, Germany, Austria, and Italy. Each destination along the route provides a distinct cultural experience, from medieval towns and Roman ruins to scenic countryside and bustling cities. The Amber Route not only connects us to our shared heritage but also offers a timeless journey through the heart of Europe.

Leave a Reply